The average was an 18 percent drop in their excess weight.
Living With Your Pacemaker
Scott Shikora. Arlington, N.
The system uses an electrical pulse generator, a little larger than a silver dollar, that is placed under the skin in the abdomen and connected to the stomach with two wires. Implanting it takes less than an hour and is done as an outpatient laproscopic procedure. Available in Europe The device is already on the market in Europe but is still years away from Food and Drug Administration approval in the United States.
After installing the pacemaker, doctors crank up the power until patients feel unpleasant symptoms, such as nausea or cramps, then turn it down a bit until all sensation disappears. I just eat different now. Weight reduction varied widely. While about one-third in the study lost nothing, some had stunning success.
Top Navigation
One patient lost percent of her excess weight, meaning she now weighs slightly less than her ideal. Placebo effect? Some have wondered whether the benefits are due to a placebo effect, since patients wanted to lose weight and knew they were being treated.
After getting the device, she failed for a year and a half to lose weight. Then doctors discovered one of the wires had come loose. After they reattached it, she dropped almost pounds. Surgeons are still unsure exactly why it deadens appetite.
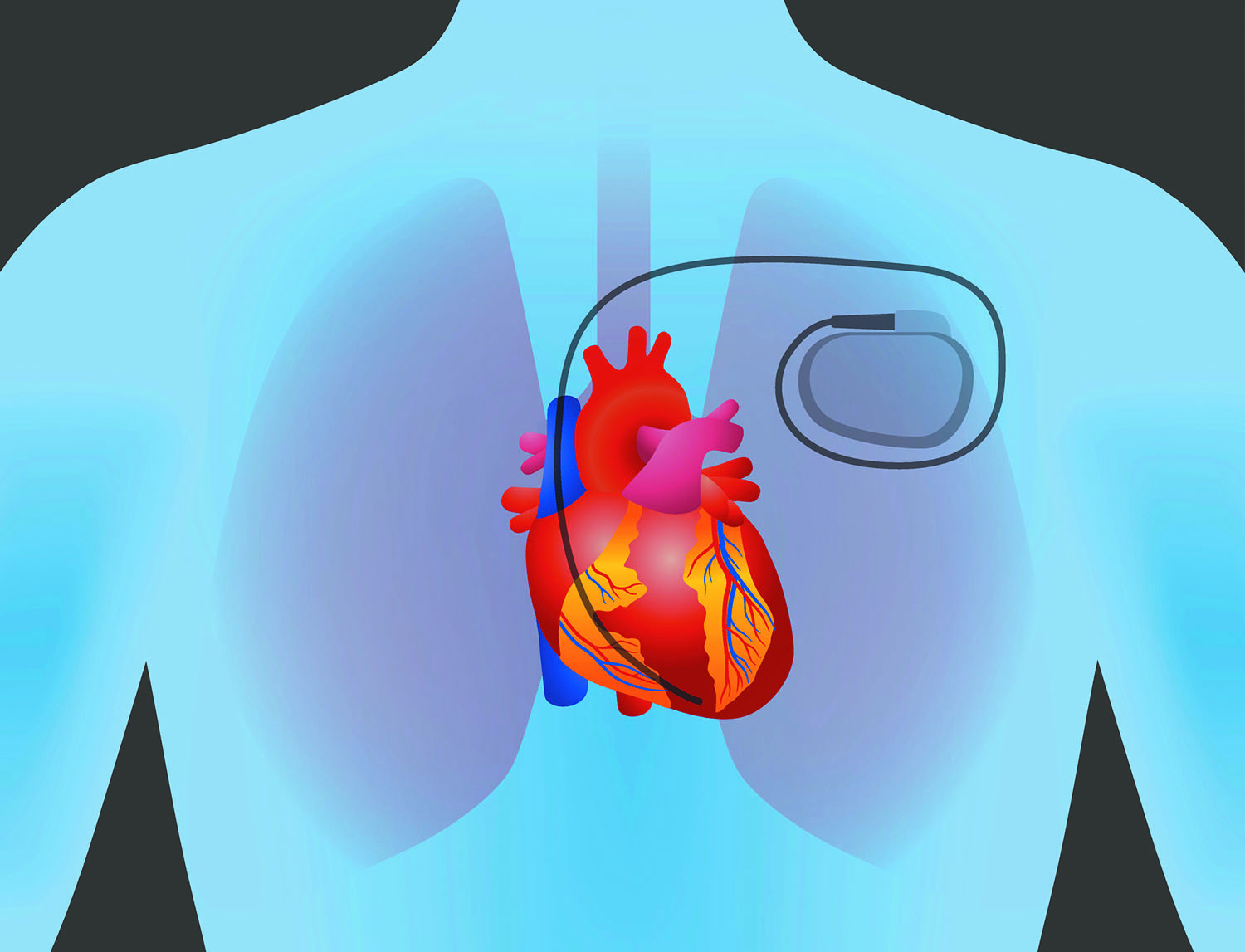
How a Pacemaker Can Give Your Heart New Life
When the heartbeat is abnormal, the programmed pulse from the pulse generator travels along the leads to your heart muscle and makes the necessary heartbeat correction. You'll probably have your first pacemaker check-up a few weeks after the surgery. Although pacemakers are generally safe, complications — although rare — can occur.
These include. Another type of pacemaker now available is implanted through a vein in the leg and placed at the tip of the right ventricle at the bottom of the heart.
However, this device is for patients who only need the bottom chamber of the heart paced. Electromagnetic equipment in everyday life may interfere with pacemakers if used too close to the body, according to a study published online Feb. However, the risk of causing harm is quite small when the device settings are properly programmed. Researchers tested the impact of electric and magnetic fields EMFs on patients with pacemakers.
They found pacemakers may be susceptible to EMFs generated by power lines, household appliances, electrical tools, and entertainment electronics. EMF interference could potentially cause a temporary slowing of the heart rate, which could cause fatigue, dizziness, or fainting.
However, the researchers noted the risk of interference can be minimized by lowering the sensitivity of the pacemaker and keeping a safe distance from EMFs — about a forearm's length away longer than 12 inches. Disclaimer: As a service to our readers, Harvard Health Publishing provides access to our library of archived content.
How a Pacemaker Can Give Your Heart New Life | www.nurseryhills.com
Please note the date of last review or update on all articles. No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician. Harvard Men's Health Watch. Today's versions can correct many types of heart conditions that can keep you active and help you live longer.
Published: October, E-mail Address. First Name Optional.